Bot Management in the Era of AI – A Buyers’ Guide

Why Bot Management Is Critical for Organizations
The use of automation by both basement hackers and sophisticated cybercriminals is scaling faster than ever, eroding digital trust and putting businesses at risk. Fake accounts, synthetic traffic, and fraud are becoming more deceptive and challenging to detect—and more costly to ignore.
Understanding Kinds of Bot Attacks
What Is a Bot?
A bot (short for “robot”) is a software script or program designed to perform automated tasks. Bots are programmed to execute specific actions quickly and efficiently, often mimicking human behavior to interact with users, systems, or other programs.
Are All Bots Malicious?
No. There are many types of bots that can be beneficial to organizations. “Good” bots perform useful functions and automate repetitive tasks. However, bots can also be used by bad actors to engage in malicious or unethical behavior that harms users, businesses, or systems for personal gain or disruption.
How to Know If You Have a Bot Problem
Bot attacks can be executed on web and mobile apps and application programming interfaces (APIs). There are a few basic warning signs that can serve as potential indicators that you have a bot problem.
• Hundreds or thousands of login or checkout attempts
This kind of activity can indicate that a credential stuffing or carding attack is taking or has taken place.
• Inhuman user behaviors
Simple bots scroll sites more quickly and precisely than humans do, though it is important to note that sophisticated bots mimic human behavior.
• Spikes in password reset requests
After fraudsters take over an account, they immediately change the password.
• Spikes in help desk calls
Consumers will likely contact customer support if they are notified of an unauthorized login to their account or if they are locked out of their accounts because of an unauthorized password change.
• Unusually high numbers of chargeback requests
This kind of activity can indicate someone is buying with an unauthorized account.
• Spikes in shipping address changes
This can indicate an account has been compromised by shipping fraud, where criminals use drop-shippers (entities that sell products that aren’t in stock) or mules (accounts for money laundering) to forward illegal purchases.
• Spikes in average purchase item price
Criminals often buy expensive items to make more money with fewer purchases to reduce the risk of being discovered.
• Multiple, rapid-fire changes to accounts
This is a major red flag of account fraud. Users rarely need to change their payment information, address, and password at the same time.
• Spikes in reward points activities
Fraudsters redeem bonuses for merchandise or services, drain them to sell on the dark web, or add them to their accounts.
• Anomalous IP patterns
An increase in IPs associated with multiple devices, multiple accounts, or pointing into untraceable ranges can indicate that a fraudster is manipulating IPs.
• Slow application response time
Some bot attacks unleash large numbers of requests that overwhelm your application and congest your content delivery network (CDN).
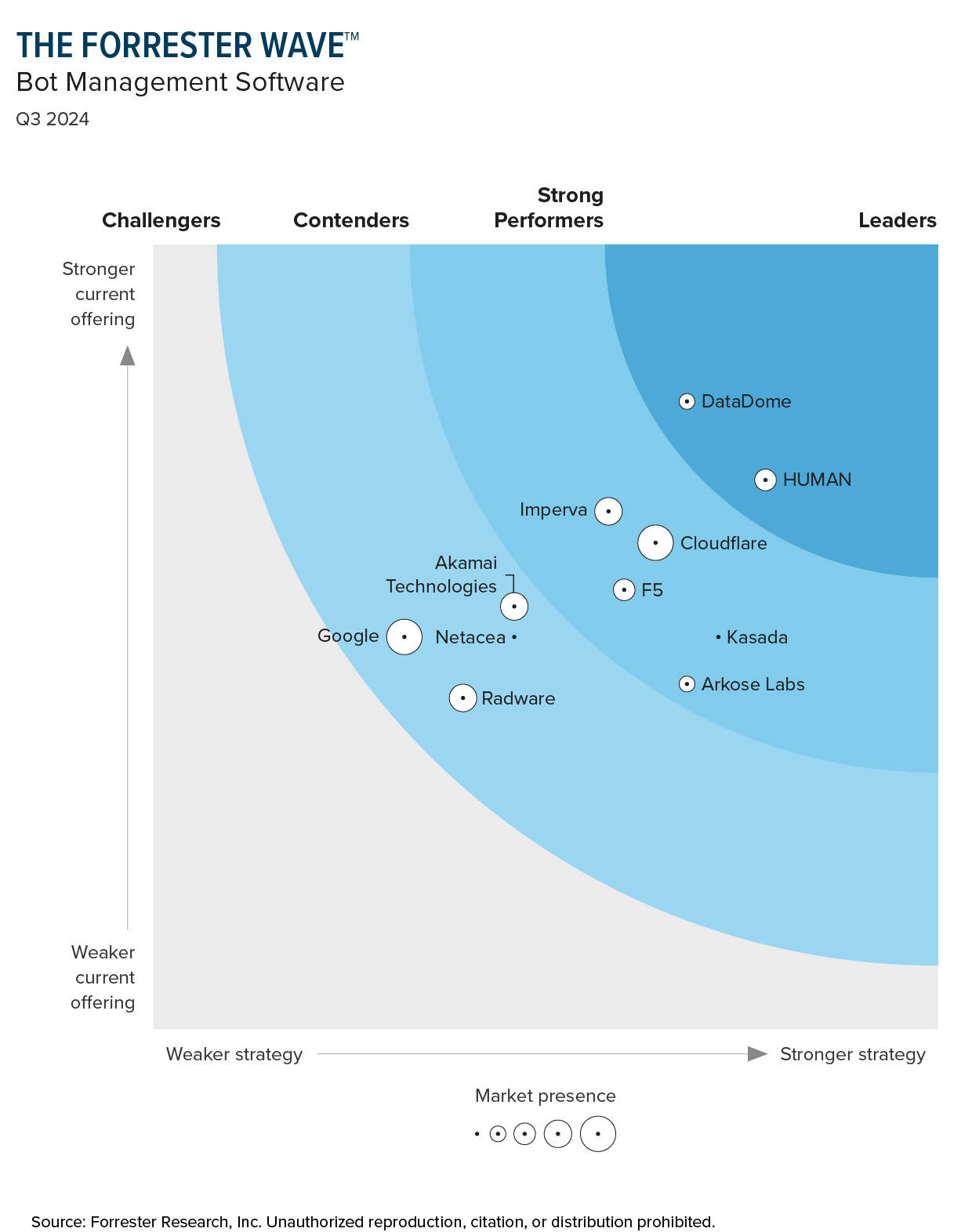
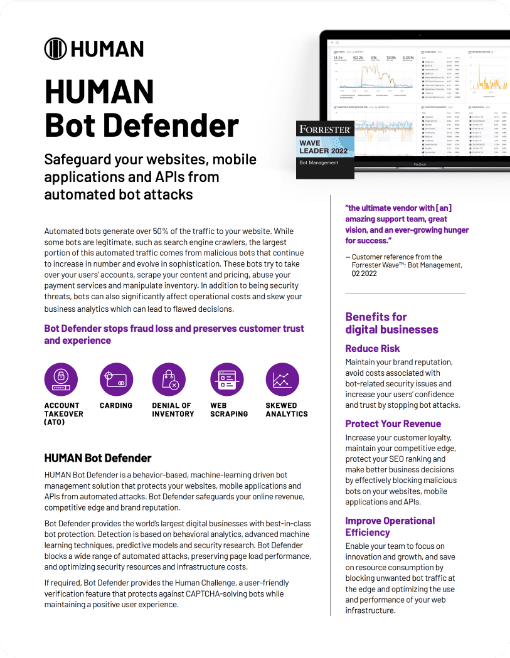
HUMAN Security: A Bot Management Leader
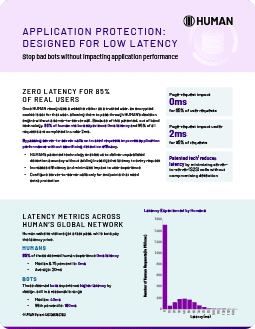
HUMAN was named a Leader in The Forrester Wave™: Bot Management Software, Q3 2024. Our Application Protection package defends against malicious bots on web and mobile applications and APIs.
Make a trusted customer experience your competitive advantage.

Scale

Speed

Decision Precision
Demo the Industry Leader in Bot Management
The bot management landscape is dynamic and complex. HUMAN Security can help determine the optimal solution for your business objectives and infrastructure environment.